Information Research, Vol. 7 No. 1, October 2001,


Information Research, Vol. 7 No. 1, October 2001, | ||||
 |
 |
|||
The subject of Brazil was analyzed within the context of the French database DocThéses, comprising the years 1969 -1999. The data mining technique was used to obtain intelligence and infer knowledge. The objective was to identify indicators concerning: occurrence of thesis by subject areas; thesis supervisors identified with certain subject areas; geographical distribution of cities hosting institutions where the theses were defended; frequency by subject area in the period when the theses were defended. The technique of data mining is divided into stages which go from identification of the problem-object, through selection and preparation of data, and conclude with analysis of the latter. The software used to do the cleaning of the DocThéses database was Infotrans, and Dataview was used for the preparation of the data. It should be pointed out that the knowledge extracted is directly proportional to the value and validity of the information contained in the database. The results of the analysis were illustrated using the assumptions of Zipf's Law on bibliometrics, classifying the information as: trivial, interesting and 'noise', according to the distribution of frequency. It is concluded that the data mining technique associated with specialist software is a powerful ally when used with competitive intelligence applied at all levels of the decision -making process, including the macro level, since it can help the consolidation, investment and development of actions and policies.
The storage capacity and use of databases has increased at the same rate as advances in the new information and communication technologies. Extracting relevant information is, as a result, becoming quite a complex task. This 'panning for gold' process is known as Knowledge Discovery in Databases - KDD.
KDD can be regarded as the process of discovering new relationships, patterns and significant trends through painstaking analysis of large amounts of stored data. This process makes use of recognition technologies using statistical and mathematical patterns and techniques. Data mining is one of the techniques used to carry out KDD. Specific aspects of the technique are: the investigation and creation of knowledge, processes, algorithms and mechanisms for recovering potential knowledge from data stocks (Norton, 1999).
The discovery of knowledge in databases, KDD, is regarded as a wider discipline and the term 'data mining' is seen as a component concerned with the methods of discovery and knowledge (Fayyad et al., 1996).
The application of data mining permits testing of the premise of turning data into information and then into knowledge. This possibility makes the technique essential to the decision -making process. In order to achieve this result it is necessary to investigate the effective use of knowledge obtained by data mining in the decision -making process and the impact it has on the effective resolution of problems and on planned and executed actions.
This study intends to demonstrate the application of the data mining technique, using as a case study the DocThéses database, a catalogue of French theses. The study focuses on theses dealing with Brazil and includes also theses by Brazilians defended in France. The period studied is 1969 -1999. The parameters of the study were:
Included in the concept of data mining (DM) are all those techniques that permit the extraction of knowledge from a mass of data which would otherwise remain hidden in large databases. In the first stage of DM we have pre-processing, in which data are collected, loaded and 'cleaned'. In order to do this successfully, it is necessary to know the database, which involves understanding its data, the cleaning process and preparation data in order to avoid duplication of content as a result, for example, of typing errors, different forms of abbreviation or missing values.
Data mining tools identify all the possibilities of correlation that exist in databases. By means of data-exploration techniques it is possible to develop applications that can extract from the databases critical information with the aim of providing maximum possible assistance in an organization's decision-making procedures.
The concept of data mining, according to Cabena et al. (1997) is: the technique of extracting previously unknown information with the widest relevance from databases, in order to use it in the decision-making process.
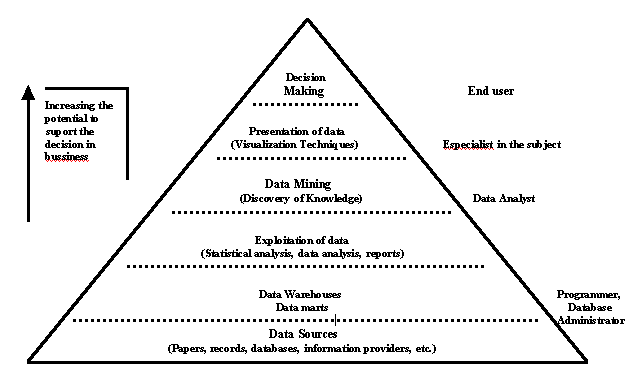
Figure 2 shows the logical placing of the different phases of decision -making with their potential value in the areas of tactics and strategy. In general, the value of information to support the taking of a decision increases from the lower part of the pyramid towards the top. A decision based on data in the lower levels, in which there are usually millions of data items, has little added value , while that which is supported by highly abbreviated data at the upper levels of the pyramid probably have greater strategic value.
By the same token, we find different users at the different levels. An administrator, for example, working at an operational level, is more interested in daily information and routine operations of the 'what' type, found in records and databases at the bottom of the information pyramid. This information creates data. On the other hand, business analysts and executives responsible for showing the way forward, creating strategies and tactics and supervising their execution, need more powerful information. They are concerned with trends, patterns, weaknesses, threats, strong points and opportunities, market intelligence and technological changes. They need 'why' and 'and if' information. They need internal and external information. They are the creators and those who demand data analyzed with a high level of value added, information from the top of the pyramid.
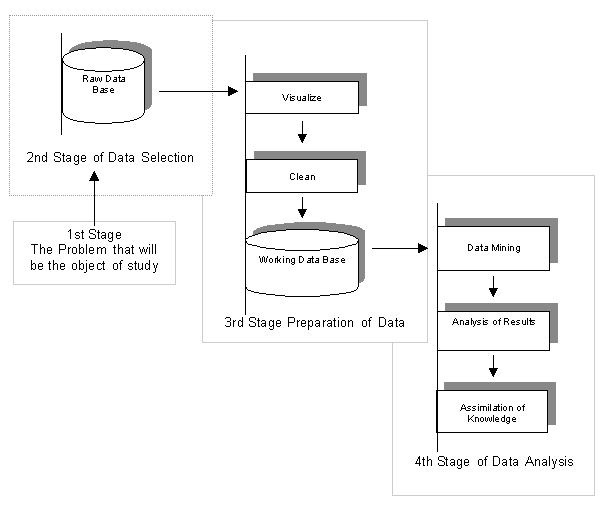
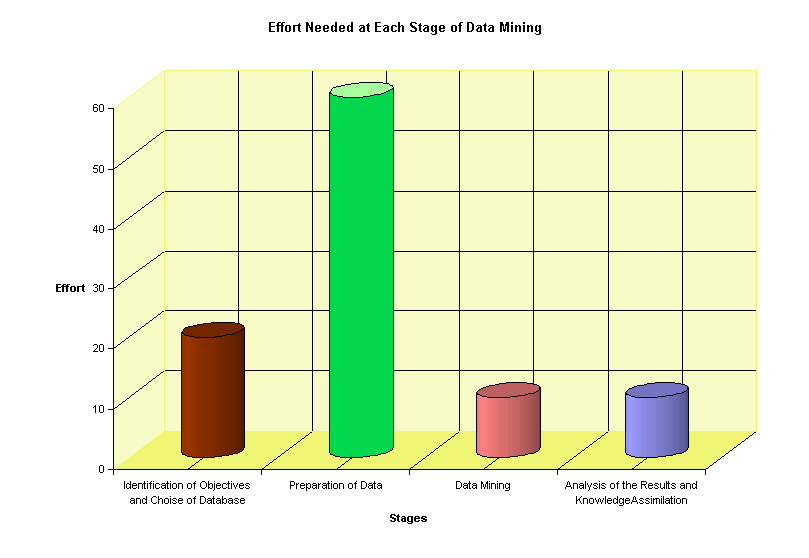
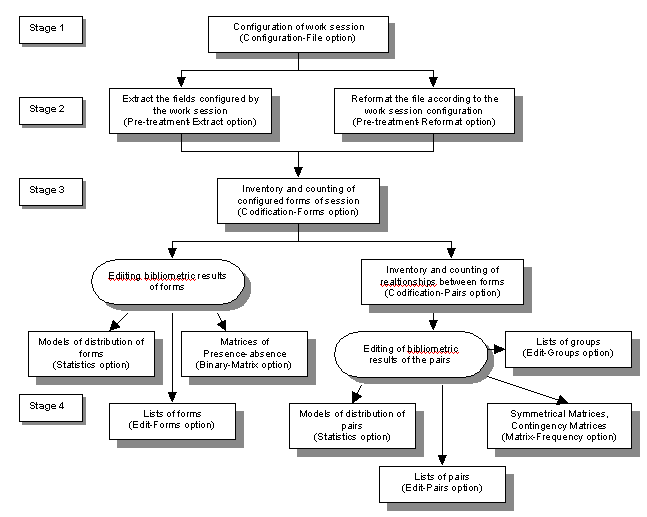
A general view of the stages involved in DM is shown in Figure 3. The process starts with a clear definition of the problem - stage 1, followed by stage 2, which is the selection process aimed at identifying all the internal and external sources of information and selecting the sub -group of data necessary for the application of DM, to deal with the problem. Stage 3 consists of preparing the data, which includes pre -processing, the activity that involves the most effort. It is divided into visualization tools and data reformatting tools, which make up 60% of DM, a situation illustrated in Figure 4. This preparation is crucial for the final quality of the results and because of this, the tools used are very important. The software used at this stage must be capable of performing many different procedures, such as adding values, carrying out conversions, filtering variables, having a format for exporting data, working with relational databases and mapping entry variables. In general these stages resemble the information cycle or the information management process carried out within the thematic area of Information Science, particularly in the information retrieval process.
We now pass on to stage 4 in the analysis of results obtained through the DM process, two basic aspects of which have to be considered: giving information about new discoveries and presenting them in such a way that they can be potentially exploited. In this phase the participation of an expert in the area of databases is recommended in order to answer specific technical questions that may influence the analysis. Business managers and executives may be involved at this stage.
By applying data mining we may achieve various kinds of knowledge discovery. Among these, the discovery of associations, discovery of groupings, discovery of classifications, discovery of forecasting rules, classification hierarchies, discovery of sequential patterns, and discovery of patterns in categorized segmented and time series, which are found in Alvares (2000).
The Database chosen to study data mining was DocThéses, the catalogue of theses defended in French universities. This catalogue is the responsibility of the Agence Bibliographique de l'Enseignement Supérieur - ABES, connected to the Department of Research and Technology of the French National Ministry of Education and its aim is to supply the University Documentation System, to locate and register the documentary resources of higher education libraries and also to monitor the regulation of cataloguing and indexing texts.
The DocThéses database is available on CD -ROM and the year 2000 version was used for this study. Theses that had Brazil as their research topic were extracted. The total sample was 1,355 theses (bibliographic records), among which were also included all theses written by Brazilians and defended in France between 1969 and 1999.
The format for each bibliographic reference (occurrence) followed the following structure:
We chose to study various tendencies in procedure, created and chosen by means of applying the Dataview bibliometric software which will be the object of commentary and analysis in subsequent sections of this study.
After the data preparation stage in which Infotrans Version 4.07 software was used, and once the working database had been prepared, we began data mining using Dataview, bibliometric software for extracting trend indicators developed by the Centre de Recherche Rétrospective de Marseille - CRRM of the Aix -Marseille III University, St. Jérome Centre, Marseilles, France.
Dataview is based on bibliometric methods whose ultimate objective is to turn data into intelligence for decision -making by creating elements for statistical analysis. To achieve this, reformatting data is a basic condition for bibliometric treatment. After statistical analysis the information retrieved will have a decisive influence on generating knowledge and intelligence, a process in which two aspects will be considered.
Both value and validity of information will have a decisive influence in the search for knowledge in databases (KDD). This is the philosophy which must direct any study concerning data mining as well as generating knowledge. When applying Dataview it became obvious the importance of the previous phase of preparation of data (data cleaning) done with Infotrans. The quality of the data generated by Infotrans did result in clear results from the bibliometric analysis.
In Figure 5 we present the situation of Dataview in a bibliometric study. Another important characteristic of the Dataview software relates to the measurement characteristic of bibliometry established on numerical bases which in their turn are created by using occurrences. Thus, for each unit of bibliographic element, occurrence must be dealt with in three ways, a) primary state - simple location of occurrences, presence or absence of reference elements, b) condensed state - expansion of these occurrences or frequencies, and c) co -occurrence, which represents the combination of primary and condensed states. In this way lists will be created - occurrence frequency and co -occurrence and frames - frameworks of presences and absences (Rostaing, 2000).
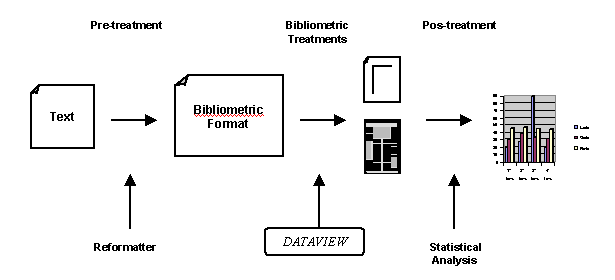
In Figure 6 we show a schematic view of the stages of a work session in Dataview.
To gain an understanding of data it is important to know the three basic laws of bibliometry:
1) Bradford's Law (or the Law of Dispersion): concentrates on the repetitive behavior of occurrences in a specific field of knowledge. Bradford chose periodicals for his analysis because of their characteristics of occurrence of themes and tendencies, and found that few periodicals produce many articles and many periodicals produce few articles.
2) Lotka's Law: analyses writers' scientific production, that is, it measures the contribution of each of them to scientific progress. Lotka's Law states the following: the number of writers who produce n works is in the proportion of 1/1 raised to n2 of writers who produce only one work;
3) Zipf's Law: is called the fundamental quantitative law of human activity. It is sub -divided into Zipf's First Law which relates to the frequency of words appearing in a text (number of occurrences of words). It is controlled by the following mathematical expression:
Where K = constant; R = word order, and F = word frequency.
Zipf's Second Law identifies low-frequency words that occur in such a way that several words show the same frequency (Tarapanoff, Miranda & Araújo Jr., 1995).
For this study, we shall look at the Zipf curve in the light of the Figure below:
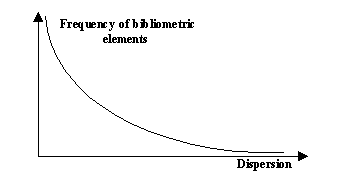
According to Quoniam (1992), on the Zipf curve we have:
Zone I - Trivial information : defining the central themes of the bibliometric analysis;
Zone II - Interesting information: found between Zones I and II and showing both peripheral topics and also potentially innovative information. It is here that technology transfers related to new ideas should be considered, and
Zone III - Noise: characterized by containing concepts that have not yet emerged in which it is impossible to say whether they will emerge or if they will remain merely statistical noise.
Zones I, II and III are represented on the Zipf curve as shown in the following Figure:
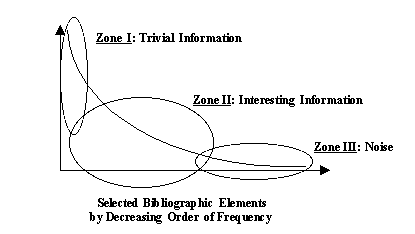
Starting from this reference point, we chose to present the results of the data mining exercise as applied to the DocThése database taking into account only Zones I and II by reason of their ability to define the central themes of the bibliometric analysis and of potentially innovative information, respectively.
The results are presented in the following section.
A third of the total of theses which had Brazil as either the researcher's country of origin or as the topic of research, were found in the areas of economics, sociology and technological sciences, closely followed by 101 and 98 theses in the areas of geography and biology respectively, as may be seen in Graph I and which corresponds to Zone I - Trivial information.
As France, together with Germany, has one of the most important and longstanding schools of sociology, it is therefore a favorable location for the elaboration of academic studies in this area, as is shown in Graph I. The same is true of economics, where we also find a strong interest in Latin American topics. These are topics that students researching Brazil look for and are of constant interest.
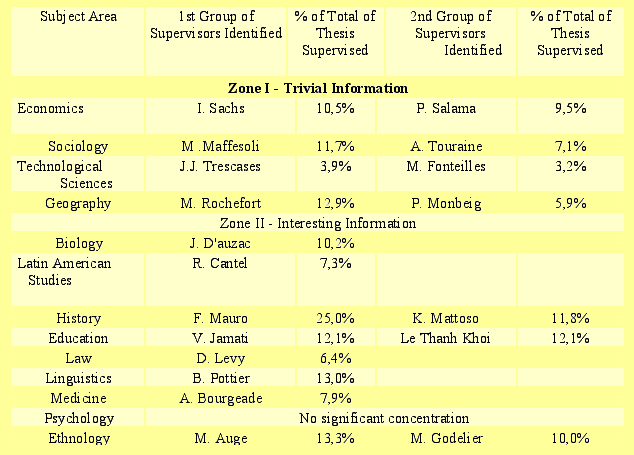
In terms of the area of technology, France is one of the world leaders in technological development, having an efficient system of technological innovation that justifies its position in the rankings of this field of research. Of the supervisors represented in these areas, Table 1 shows that production is concentrated around those lecturers who together account for 20%, 18% and 7.1% of the total number of theses defended.
It should be pointed out that the areas analyzed were those in which the numbers of Brazilians in France grew during the period up to 1994, after which time there was a decline in demand.
Zone II - Interesting information, in its turn, represents those areas that are emerging, which is indicated by the areas of education, medical sciences, Latin American studies and history, which have been increasing in popularity since 1995. Some of the facts that have been creating interest in these areas of study are found in the influence of the new scientific and technological dimension as is the case of the areas of education and medicine, which are constantly affected by new discoveries and technologies that move them forward in the field of human knowledge. In the case of history, the fact of our living in a period of abrupt transition in this type of society, forces us to engage in a constant re -reading and search continually for explanations concerning new aspects of this society.
Within the area of history, Fréderic Mauro stands out, because among all the supervisors, he supervised the greatest number of thesis between 1969 and 1999, with 25% of the total relative to the first group of supervisors (Zone II - interesting information), as Graph 2 illustrates. This performance results fundamentally from the strong influence of French historiography in Brazilian academic life. In the 1930s, a group from France, composed of several lecturers from different areas, brought to Brazil the eminent teacher Fernand Braudel, one of the creators of the first founding generation of the French School of Analysis which still contains important figures in historiography such as Marc Bloch and Lucien Fébvre. At this time, as a result of the French visit, the History Department of the University of São Paulo was founded, an event that began the decisive influence of French historiography in Brazil. In the particular case of Professor Fréderic Mauro, his great influence in this school of historiography, together with that of Georges Duby and Jacques Le Goff, among others, belongs to the second generation.
As a result of the facts mentioned above we may state that not only does the number of thesis supervised by Mauro account for the significant number of works noted in the area of history, but that this is also clearly due to the fact that French historiography has been the main catalyst for the interest of Brazilian historians seeking training abroad.
When we looked at the careers of researchers in France, the result was Graph 3, the results of which indicate that 62% of defended theses were presented in Paris. Of the remaining 40%, Montpellier, Toulouse, Marseilles, Grenoble and Bordeaux accounted for 50%. The remaining approximately 50% were in 30 other French towns.
By analyzing Table 3 we find that between 1974 and 1978, only the area of Law achieved high levels of interest, the greatest concentration that was found relative to all the other areas. This situation is noticeable and may be explained in part by the political circumstances prevailing in Brazil during the 1970s.
The coincidence of the high level of concentration of theses defended in France with the peak of the military dictatorship in Brazil from 1967 raised the level of interest in understanding the state of law imposed there, especially in relation to the citizen's basic rights and guarantees.
In the area of linguistics, it will be seen that it peaked between 1980 and 1984, with a tendency to recapture interest after 1995.
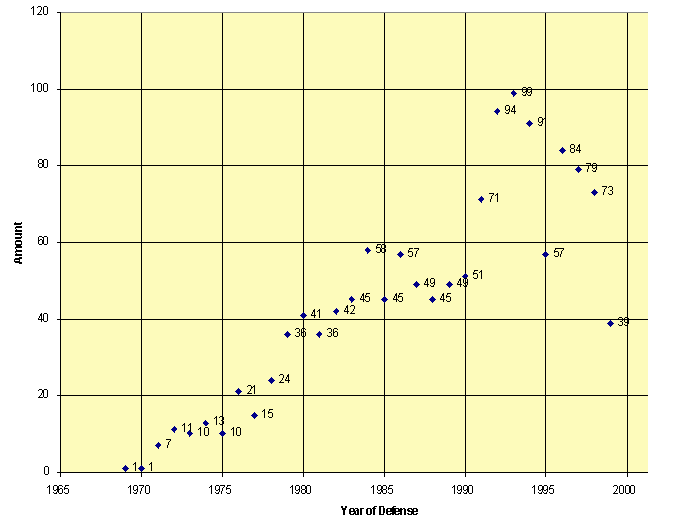
By and large, in relation to the number of thesis defended during the period in question, we may note that since 1996 the number has been falling rapidly, as may be seen in Graph 4. The reason for this is perhaps found in the fact that since 1999 there has been uncertainty about grants for overseas study in the areas of humanities and social studies, which has meant that the area of technology alone does not reach high levels as the whole.
It is interesting to note that in the period of relative equilibrium in the curve, which oscillates between 36 and 58 theses defended between 1980 and 1990, an average of about 47 theses were defended each year, with the field of economics being especially prominent during this period.
In the field of information sciences, twelve thesis were defended between 1974 and 1999. The golden age was between 1980 and 1984, with a total of five thesis. Prominent among the supervisors are F. Ballet, followed by J. Meyriat. The other five, each responsible for one thesis, were P. Albert, M. Menou, M. Mouillard, J. Perriault and G. Thibault, the latter, based in Bordeaux, being the only one working outside Paris. M. Menou has worked in information sciences as an international consultant in Canada, where he has developed several lines of research on the impact of information on development. He has developed a wide -ranging consultancy network in Brazil in conjunction with the Instituto Brasileiro de Informação em Ciência e Tecnologia - IBICT, linked to the Brazilian Government's Ministry of Science and Technology.
With regard to Zone III - the so -called zone of noise, in spite of its not yet having established emerging concepts and because it is not a very conclusive area, it must be systematically monitored since it can show, or at least allow, in the analysis of weak signals, the inference of future interests in training and research. Thus we should not dismiss it a priori. In this zone are found art and archaeology, literature, political science, science and technology, philosophy, administration, information science and communication studies, among others.
The analysis of the DocThése database in relation to retrieving the word 'Brazil' by means of data mining, was revealing with regard to the chosen subject areas, related supervisors, chronological period of major concentration of theses defended and cities chosen.
Discovery of knowledge occurred gradually as the data mining process took shape. In the first stage - defining the problem - it was decided to explore the database related to Brazil both by key -word and by origin of supervisor. The second stage - cleaning the data - brought about the first contact with the data, extracting only those of potential interest in discovering a pattern. In the third stage - carrying out the data mining per se - it was decided to use the Dataview software which already had embedded in its system statistical rules and the ability to visualize data to find knowledge. The first analyses and findings come from this phase, in line with the aim of the research. The fourth stage - analysis of data - new associations were created and knowledge emerged.
The results obtained are an illustration of how national organs for encouraging research and training high -level human resources, such as the Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento do Pessoal de Nível Superior (CAPES), and the Conselho Nacional de Pesquisa (CNPq) can direct their investments into areas of knowledge that are felt to be relevant, by means of knowledge discovered in databases. On the academic side the Brazilian Federal Universities already started to use data mining in laboratorial research and consultancy work using several softwares, among them Clementine (SPSS, 2001).
Although the utilization of data minig in Brazil still is in its initial phase, in the governmental and productive sector there are signs of its application. The Brazilian Programme of the Industrial Technological Prospective (Programa Brasileiro de Prospectiva Tecnológica Industrial) makes use of the methodology of Technology Foresight, and uses data mining on historical and current data bases to foresee probable futures.
The figures obtained and their application reinforce the aims of the data mining process by turning data into information and being used in the decision -making process of organizations that take decisions related to the preservation of and innovation in knowledge. Although economics, sociology and history are not priority areas for development in Brazil, they are essential to an understanding of the roles of the Brazilian economy, society and history, which have been strongly influenced by France from the point of view of theoretical and cultural orientation. These areas should continue to receive investment. The impact of this influence was seen in the Exhibition of the Re -Discovery of Brazil (2000), where many documents written by French travelers indicated their presence and influence in the country. Other areas such as technological sciences should be examined because they are diminishing, while areas in expansion should be examined from the point of view of elaborating bilateral technical, cultural and economic co-operation agreements.
It is impossible to deal with all the implications concerning political, technical, economic and cultural agreements that may be achieved through analyzing databases of the kind studied here. Other bases from other sources and other countries would provide different possible implications.
It is possible that the present article might be the start of a series dealing with the rise of interest in research in Brazil and other countries that seeks parallels and discovers knowledge from the results found by applying data mining as an effective managerial tool.
Contents |
|
Home |